Some of the most common types of pain experienced by people with gonarthrosis include the following.
Joint stiffness
You may have noticed knee stiffness after a long period of sitting, or when getting out of bed in the morning. In other words, you can’t move your knee easily. Often, this stiffness dissipates after 20 to 30 minutes.
Joint pain
Unlike stiffness, joint pain is more severe and occurs when you use your knee. It extends deep and gives a sensation of increased pressure throughout the joint. Rest brings relief.
Swelling
The joint tissues feel more spongy and warm to the touch, and are sometimes visibly swollen. Swelling is often related to inflammation, which causes fluid to build up in the joint.
Cracking sensations
Patients often report a “creaking” sensation in the knee bones or louder than usual cracking noises.
Joint instability and dysfunction
You notice that your knee doesn’t bend the way you want it to and doesn’t respond as well to your commands as before. Peripheral joints such as hips and ankles compensate for your pain. So it’s not uncommon to see a person with knee osteoarthritis experience ankle weakness, hip pain or other types of joint imbalances.
What causes knee osteoarthritis?
The most important factor in the development of this condition is undoubtedly age. The older we get, the harder it is for our bodies to regenerate. The tissues that make up the joints we use most over our lifetime, such as the hips and knees, are among the first to suffer.
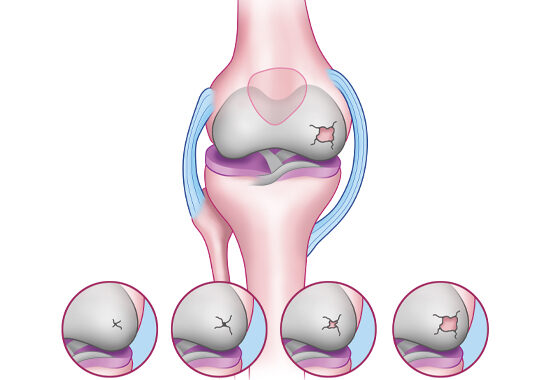
The root cause of the problem, however, is the wear and tear of cartilage. This is caused by several factors, including pressure from long-term loads, excess weight, postural defects, heredity and more.
Why is knee osteoarthritis so painful?
The cartilaginous surfaces that cover and protect joint pressure points deteriorate, exposing the bony surfaces of the knee—which are more susceptible to pain than cartilage.
How can knee osteoarthritis pain be treated?
There’s no way to “cure” osteoarthritis per se. However, treatment options are available to relieve pain and improve natural joint function.
Here are three effective ways to relieve symptoms and prevent the further progression of knee osteoarthritis.
Small changes in lifestyle
Keep moving! Low-impact activities help reduce pain and optimize mobility in a knee with gonarthrosis. Swimming, cycling, walking and ball exercises are great examples. These activities optimize the quality of the tissues that make up the joint.
Also, when moving, your knees absorb a lot of your weight. Excess weight exacerbates the pain associated with osteoarthritis. A supervised weight loss program is something to consider if you’re overweight—one that will benefit your overall health.
Use of foot orthoses
Foot orthoses are custom designed. They slip into your shoe, under your foot. They help reduce pain by alleviating pressure and redistributing the load in a way that helps the lower limb joints (including the knee).