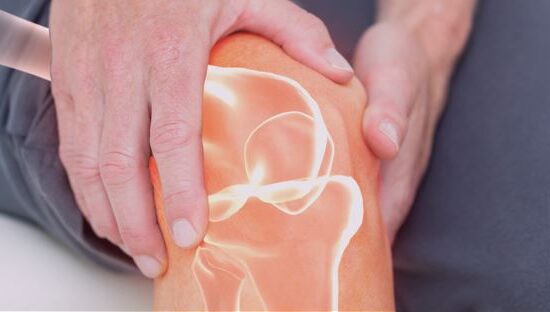
What is periostitis?
Periostitis corresponds to an inflammation of the periosteum, the fibrous membrane that envelopes and protects the bones. In the case of medial tibial periostitis, or shin splints, the most frequent type, this involves inflammation of the tibial periosteum. This ailment often occurs in people who are starting a new physical activity that particularly solicits the tibia, or in experienced athletes at the beginning of the season.
Where does it come from?
The damage is caused by repeated excessive tensions on the periosteum. Several external factors may favor the appearance of shin splints, including:
- An inadequate shoe;
- A biomechanical disorder of the foot (flat foot or cavoid foot);
- A rapid increase in the intensity of physical activity;
- A lack of flexibility or muscle weakness;
- A change of running or playing surface.
How can it be recognized?
Shin splint symptoms are manifested as an unusual pain that may appear over several centimeters in the tibial region or the inner face of the leg, during or after physical activity. The discomfort, which can be likened to a burning sensation in the bone, frequently affects runners.
If physical activity continues despite the shin splints, the pain tends to intensify. It can be alleviated by rest and the application of ice to the inflamed area.
Treatment solutions
- Opt for a foot orthosis
A foot orthosis helps eliminate shin splint symptoms by correcting biomechanical foot disorders, if applicable. It also distributes the pressure under the foot, providing it with more support and stability, and its cushioning absorbs the shocks that could affect the tibial periosteum.
- Choose the right shoe
Many models of shoes are available, designed with specific characteristics to respond to the foot’s different biomechanical needs and the physical activity practiced. Whether the aim is flexibility, stability or shock absorption, it is important to consult an advisor to make the right choice for preventing shin splints.